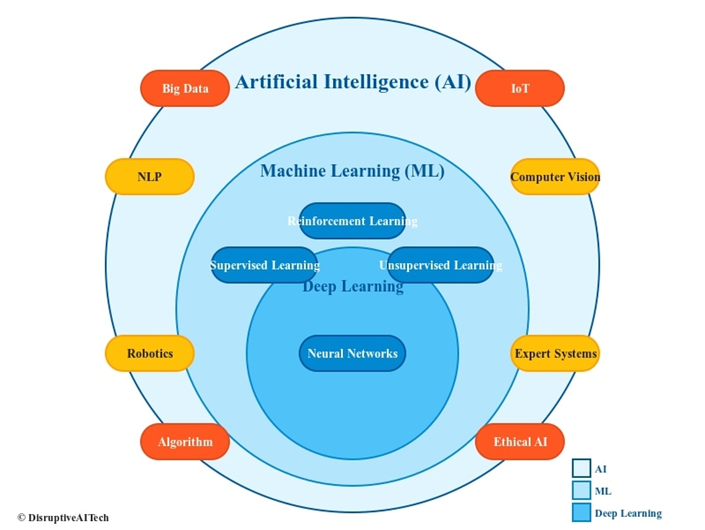
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Imagine you are playing chess with a friend. You are both making moves. But instead of playing chess, AI is a computer program that can think and learn like a human. It can make decisions, recognize patterns, and solve problems on its own.
Think of AI as a super-smart assistant that can help you with tasks like finding the best route home, recommending movies, or even chatting with you like a friend.
Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant are examples of AI in action. They can understand your voice, respond to your queries, and even make recommendations based on your preferences.
2. Expert System
An expert system is based on designing the complex logic. It’s a computer system designed to make the decision-making ability of a human beings. Expert systems follow a set of rules to make decisions or solve problems in specific areas mostly based on if-then-else constructs. Computers follow the predifined instructions to make decisions.
For example, in the game of chess if we design system to make moves based on all possible moves based then its expert system.
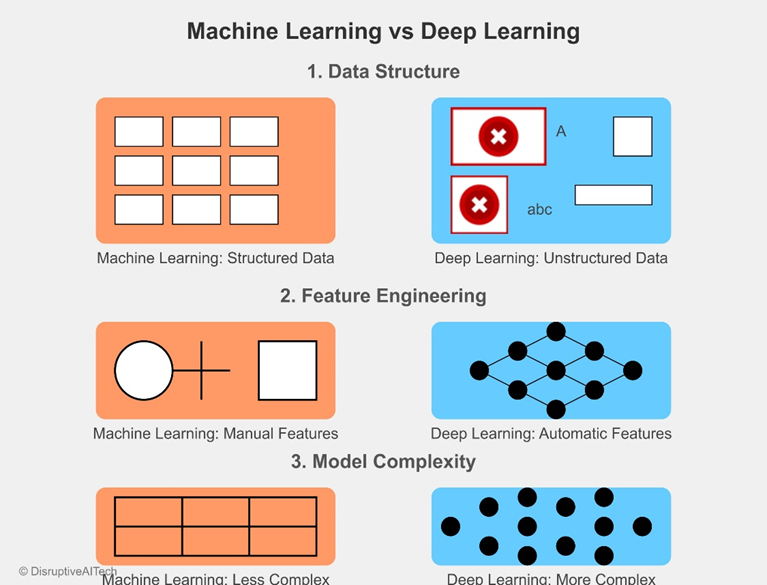
3. Machine Learning
Unlike expert systems, machine learning is like teaching a computer to learn from experience, just like we do. Imagine showing a computer thousands of pictures of cats and dogs. Over time, it gets so good at recognizing them that it can tell whether a new picture is a cat or a dog on its own.
When Netflix suggests a movie you might like, it’s because it has learned your preferences from the movies you’ve watched before.
3. Deep Learning
Deep learning is like taking machine learning to the next level. Deep learning is a type of machine learning that uses neural networks (more on that later) to analyze data. Machine learning comes intelligent by learning the patterns from the data. But, when patterns are difficult to get from the comples data, pattern recognition mechanism is divided in many layers. Hence, learning takes place using the deep mechanism of layers.
Facebook automatically tags your friends in photos using deep learning, as it can recognize faces even when they look a bit different in each photo.
4. Supervised Learning
This is like having a teacher guide the computer. You give it labelled examples, like pictures of apples and oranges with their names. The computer learns from these examples, so when it sees a new fruit, it can guess whether it’s an apple or an orange.
A spam filter learns to identify unwanted emails (spam) by being trained on examples of spam and non-spam emails.
5. Unsupervised Learning
In unsupervised learning, the computer is on its own, without a teacher. It looks for patterns in data by itself. Imagine dumping a bag of mixed candies on the table. The computer will group similar candies together without knowing their names.
Online stores group similar products together, showing you “customers who bought this also bought that” without anyone telling the system which items are similar. Understand difference between supervised and unsupervised learning in below infographic.

7. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning is like training a pet. The computer learns by trying different actions and getting rewards or penalties. Over time, it figures out the best actions to take to get the most rewards.
In video games, characters can learn to navigate a maze or defeat opponents by trial and error, gradually improving as they learn what works best.
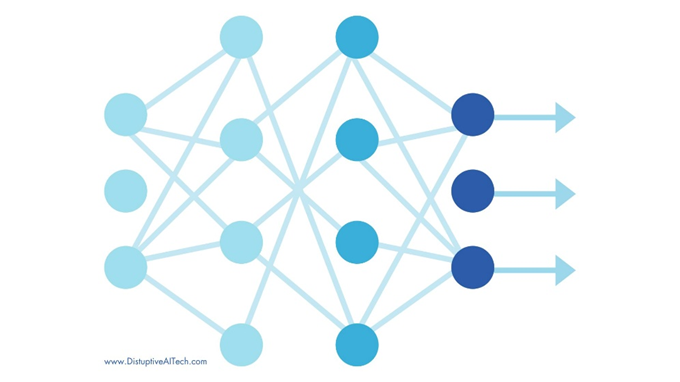
8. Neural Network
A neural network is like a simplified version of our brain. It’s made up of layers of interconnected nodes (like neurons) that process information. Each layer transforms the input in some way, helping the computer understand complex data.
Neural networks are used in speech recognition, like when your phone turns your voice into text.
9. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is all about teaching computers to understand and communicate in human language. It’s like having a translator who can speak computer and human languages.
When you ask Alexa to play your favorite song, NLP helps it understand your request and play the right track.
10. Computer Vision
Computer vision is like giving a computer eyes. It allows the computer to see and understand images or videos, like recognizing objects, faces, or even actions.
Self-driving cars use computer vision to see the road, recognize traffic signs, and avoid obstacles.
11. Algorithm
An algorithm is like a recipe for the computer. It’s a set of instructions that tells the computer how to do something step by step.
Example: The steps your GPS takes to find the fastest route to your destination is an algorithm.
12. Big Data
Big Data refers to extremely large sets of data that are too big to handle with traditional methods. It’s like trying to organize every grain of sand on a beach. The key is not just having a lot of data but being able to analyze it to find valuable insights.
Social media platforms analyze Big Data to understand trends and what people are talking about worldwide.
13. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT is like giving everyday objects the ability to connect to the internet and talk to each other. It’s as if your fridge could remind you to buy milk or your lights could turn on when you’re about to arrive home.
A smart thermostat that adjusts the temperature based on your daily routine is part of the IoT.
14. Robotics
Robotics is about creating machines (robots) that can perform tasks, often those that are repetitive, dangerous, or require precision. It’s like building a mechanical helper that can do things faster, safer, or more accurately than humans.
Robots assemble cars in factories, ensuring each part is perfectly in place.
15. Ethical AI
Last but not least, ethical AI is about making sure that AI systems are designed and used in a way that’s fair, safe, and respects people’s rights. It’s like having rules of the road for AI, so it doesn’t cause harm or make unfair decisions.
Ensuring AI doesn’t show bias, like giving better job recommendations to one group of people over another, is part of ethical AI.